imperative, OO / Java
Representation
Collected by Matthias Hauswirth — Own practice
Makes explicit the fact that logic expressions have the same structural properties as the well known arithmetic expressions.
| PL | NM |
|---|---|
| ... | (all aspects from 1-Arithmetic) |
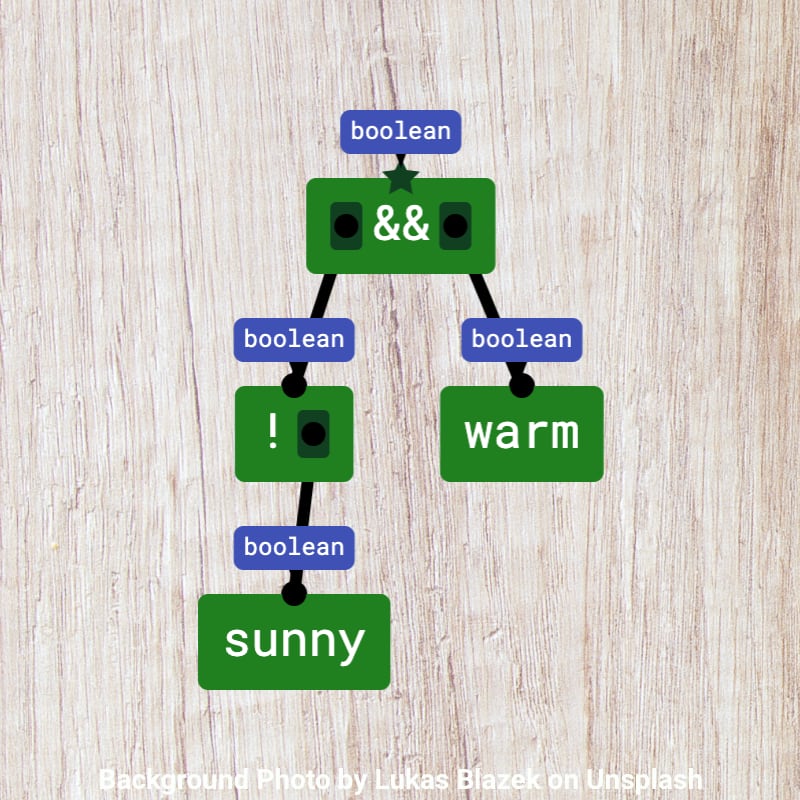
| Boolean literal | leaf tree node labeled with true or with false |
| variable | leaf tree node labeled with name of variable of type boolean |
| unary negation operator (!) | tree node with operator in front of a hole |
| binary logical operator (|, &, ||, &&) | tree node with operator between two holes |
The structure, typing, and evaluation of expressions involving logic operators and Boolean literals.
To reason about the structure and semantics of simple logic expressions.
Small, can be done on paper or with a tool like Expression Tutor.
The following videos and activities come from ExpressionTutor.org, where you can find a much more comprehensive set of resources and tools. Expression Tutor supports many different programming languages, but the material discussed here is specific to Java.
The Crash Course: Expressions in Java provides a learning experience that corresponds to this notional machine sequence.
The following video comes from section Logic of the Crash Course.
Here is an example “Expression Tutor” activity. Can you solve it?
Do you have feedback on this notional machine? Did you find a mistake, or do you have a request for improvement? You can create an Issue on GitHub, where the description is hosted. This way we can see your feedback and address it.
For this, you need a GitHub account. Then follow this link to see the source file of this page. In there, click the ... left of the highlighted line, then pick "Reference in a new issue".